Maintenance Notice (4:30 AM - 11:00 AM December 21, 2024): This website is scheduled to be unavailable due to maintenance. We appreciate your patience and understanding.
Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.197
Maximum quantity allowed is 999

Electrophoresis is a technique which separates charged biomolecules based on the rate at which they migrate in an applied electrical field. In many cases, electrophoresis of proteins are performed using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE).1) For molecular weight estimation and purity determination of proteins, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-PAGE is frequently employed. SDS is a strong denaturant of proteins and is added to samples, gels, and buffer solutions for electrodes when proteins are separated with electrophoresis. As SDS not only denatures protein but also binds to the protein, when SDS is used in conjunction with a reducing reagent such as 2-mercaptoethanol to cleave disulfide bonds in the protein, and the protein is completely denatured, the amount of SDS bound is almost always proportional to the molecular weight of the protein. Resultantly, the protein is negatively charged. Therefore, the denatured protein can be separated by molecular weight independently of its structure and biological properties.
Laemmli’s method is the most widely used system of SDS-PAGE.2) In this method, the separation and the stacking gel contain Tris-HCl and the upper and lower buffer reservoirs contain Tris-glycine. All components of the system contain SDS. The advantage of Laemmli’s method is that it gives sharper bands in the final plate.1)
Sample buffers are available in three different concentrations to allow for easy use with any sample volume. No reducing agent is included-add as required. A red sample bufferis also available to help prevent sample mix-up.
Electrophoresis samples were prepared and applied to acrylamide gels using each of the following sample buffers.
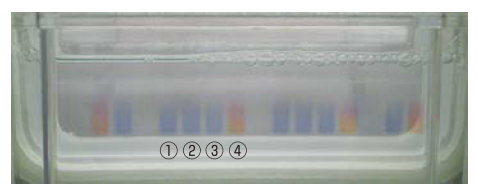
Figure. View during gel application using four sample buffers
① 2X SDS-PAGE Sample Buffer (Product No. B5834)
② 4X SDS-PAGE Sample Buffer (Product No. B6104)
③ 6X Sample Buffer (Product No. B6105)
④ 2X SDS-PAGE Sample Buffer Phenol Red (Product No. B6110)
Detecting protein bands in a polyacrylamide gel after electrophoresis requires the gel to be stained. Common staining methods include Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining, silver staining, fluorescence staining, and negative staining.
Silver staining is a commonly-used method for the detection of proteins and DNA in polyacrylamide gels after electrophoresis.3) In this method, silver ions are bound to proteins and DNA present in the gel and reduced, resulting in stained bands. Silver staining is more sensitive than Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining; it can detect down to nanogram amounts of protein.

Figure. Product Appearance of I1309
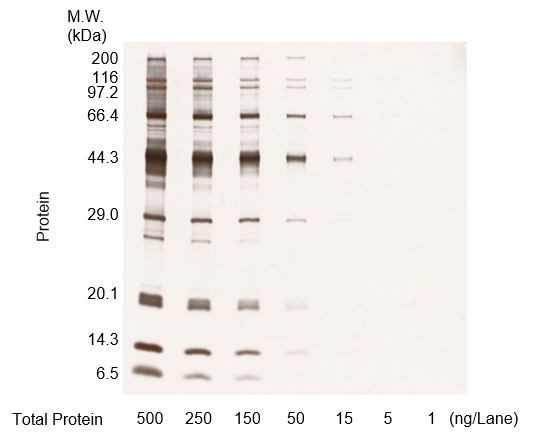
Figure A. Protein molecular weight markers were diluted, run on an acrylamide gel, and stained
(500 ng/lane, 250 ng/lane, 150 ng/lane, 50 ng/lane, 15 ng/lane, 5 ng/lane, 1 ng/lane)
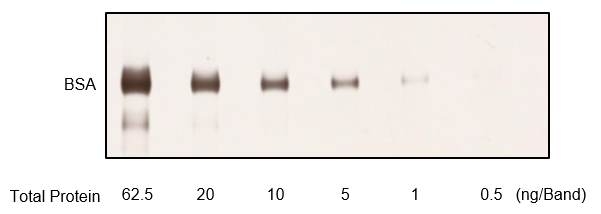
Figure B. BSA was diluted, run on an acrylamide gel, and stained
(62.5 ng/band, 20 ng/band, 10 ng/band, 5 ng/band, 1 ng/band, 0.5 ng/band)
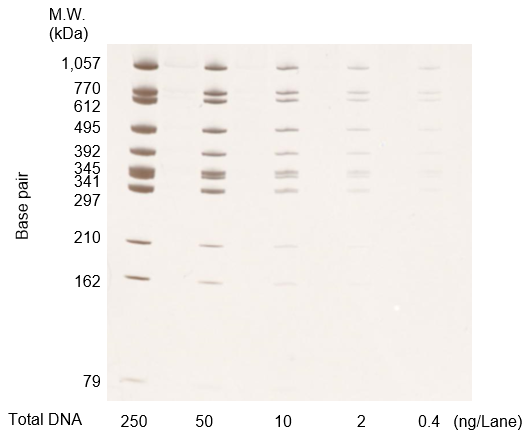
Figure C. DNA molecular weight markers at each concentration were diluted, run on an acrylamide gel, and stained
(250 ng/lane, 50 ng/lane, 10 ng/lane, 2 ng/lane, 0.4 ng/lane)
Negative staining is a method in which only regions of gel containing protein remain unstained, while the remainder of the gel is stained white.4) Bands can be visualized by placing the gel against a dark background.
Gel Negative Stain kit can be used to detect protein bands with high sensitivity in as little as 20 minutes. Furthermore, stained gels can easily be destained using the included destaining solution, with the destained gel is able to be used in further downstream applications, such as Western blotting and mass spectrometry.5,6)

Figure. Product Appearance of G0615
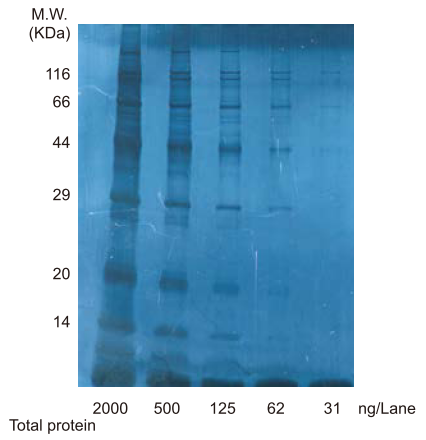
Figure. Photograph of gel stained by G0615
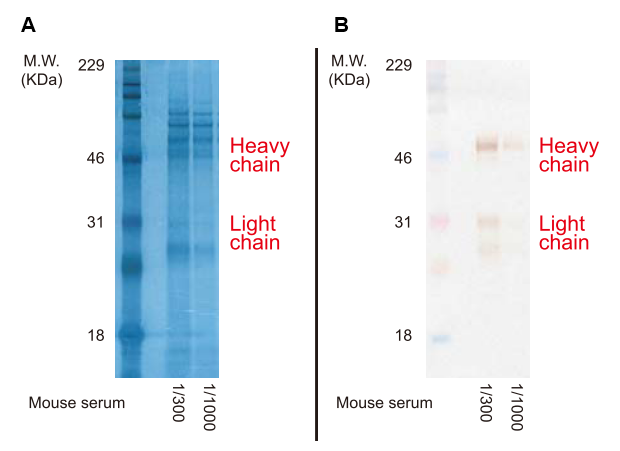
Figure. A: Gels loaded with mouse serum and stained with G0615.
B: The gel in A was destained and mouse IgG was detected via Western Blotting.
C3488 is a methanol- and acetic acid-free one-component ready-to-use solution for staining proteins. After polyacrylamide gelelectrophoresis, C3488 can be used for protein staining by soaking the gel in C3488.
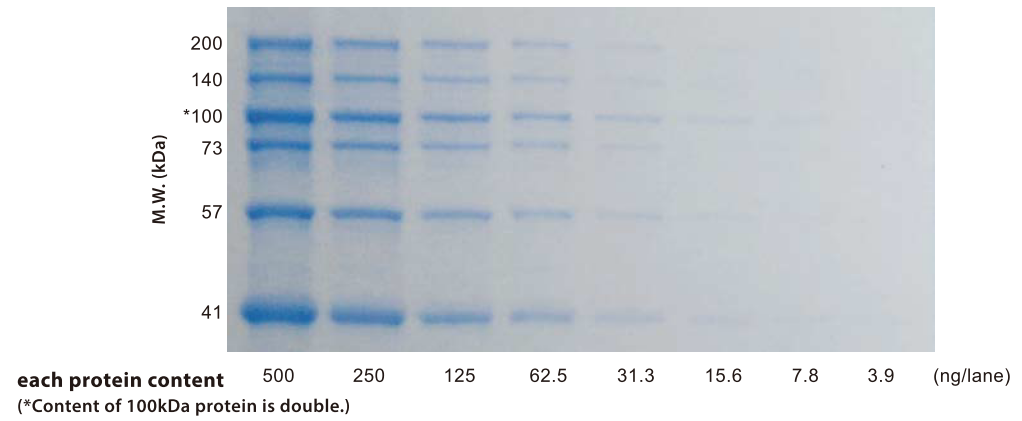
Figure. Proteins stained by C3488 (destained overnight)
| Staining Reagent | Time | Detection sensitivity | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver Stain (Product No. I1309) | ~1 hour | Several ng | Highly sensitive detection method with ample track record. Able to detect both protein and DNA. |
| Negative Stain (Product No. G0615) | 15 - 30 minutes | Several ng | Short staining time. Stained gels can be used for Western blotting, etc. |
| CBB Stain (Product No. C3488) | 2 hours - over night | Several µg | Easy-to-use, simple protocol. Resultant bands are quantifiable. |
Agarose gel electrophoresis is one of the most common methods used to size-separate and analyze DNA. The nucleotides that make up DNA carry a negative charge due to their phosphate groups, and are therefore attracted to the anode when run on an agarose gel. As the DNA moves through the gaps in the mesh of the agarose gel, longer molecules, with higher molecular weights, move more slowly, while smaller molecules are able to move more quickly. This method, of separating molecules by size on a gel using electricity, is known as gel electrophoresis.6)
Ethidium bromide is widely used as a DNA staining agent with agarose gels and can detect DNA with high sensitivity through visualization using UV light.7) However, its carcinogenicity6) means it must be handled with care. E1363 comes in a dropper bottle pre-dissolved, making it safe and easy to use.
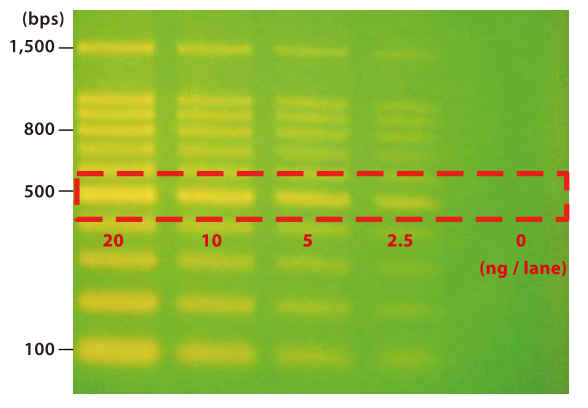
Figure. DNA Ladder Marker stained by E1363 (destained 15 minutes)
Nucleic acid stain blue is used to stain nucleic acids after agarose gel electrophoresis. As nucleic acids are stained blue, no transilluminator or other detection device is required. Unlike ethidium bromide, it is non-mutagenic and therefore safe and easy to handle.
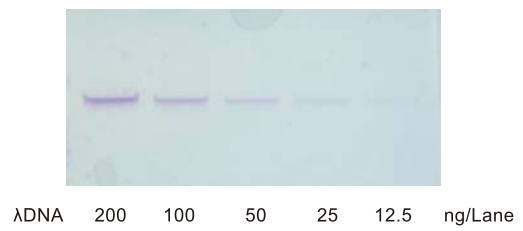
Figure. Photograph of gel stained by N1209 (destained overnight)