Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.197
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Chemistry Chat
- Focusing on the Elements - Colors and Chemical Names (1)
Kentaro Sato
Red
In the periodic table, the element whose name is derived from red is the thirty seventh rubidium. This name was coined because the color of rubidium’s emission spectrum was rubidus, meaning red in Latin. The ruby gemstone has the same name origin. As for organic compounds, there is a compound called rubyrin. A relative of porphyrin, rubyrin is composed of six pyrrole rings and shows beautiful red color.
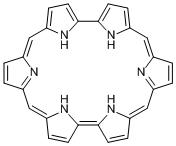
Rubyrin
Some members of anthracycline antibiotics family show red colors such as aunorubicin and doxorubicin, where the rubi in their names is derived from the color.
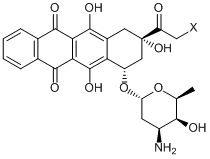
X=H: Daunorubicin, X=OH: Doxorubicin
Around 1876, it was discovered that the animal photoreceptor cells contain a reddish substance that are responsible for sensing of light. The substance was named rhodopsin by combining rhodo and opsis (which means vision). The redness is actually a result of the chemically bonded compound called retinal, which produces visual signals in the form of double bond isomerization upon photo irradiation.
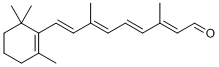
Retinal
Yellow
Yellow in Greek is xanthon and there are lots of compounds named after it. Xanthene has a structure composed of two benzene rings fused with a pyran and is literally a yellow solid.

Xanthene
Xanthophyll compounds are yellow pigments containing a long chain of conjugated double bonds and are involved in photosynthesis. This group includes compounds such as lutein, zeaxanthin, neoxanthin, violaxanthin, and cryptoxanthin. Some compounds that appear more red than yellow like astaxanthin are also found in the group.
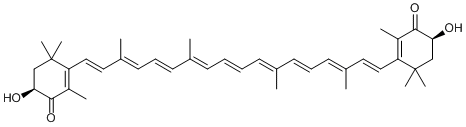
Astaxanthin
On the other hand, the Latin translation of yellow is flavum and there are compounds known that are named based on it. One of them is flavines, whose derivatives act as coenzymes, the shortage of which causes various disorders such as inflammation. Flavones sound very similar and are derived from the Latin flavus but are unrelated to flavines structurally.
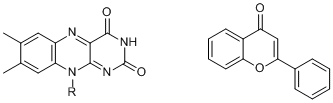
Flavines and flavones
In a similar context, the word fulvous (dull brownish yellow) can be found as part of the names of some compounds. For instance, the hydrocarbon compound shown on the left in the figure below is fulvene, which is an isomer of benzene. The compound in the middle composed of two cyclopentadienes is called fulvalene, but the one on the right, tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) with four sulfur atoms replacing the methine hydrogens, is far more well-known. TTF works as the electron donor of a charge transfer complex and is an iconic compound in the field of organic electronics materials.
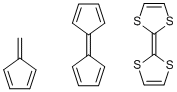
Fulven, fulvalen, and tetrathiafulvalene
There is a group of cyclic compounds called oxocarbonic acids. Three- to seven-membered ring compounds are known and all of them show strong acidity. Among these, the five-membered ring compound is yellow and called croconic acid after the Greek krokos, which means saffron or egg yolk. The six-membered ring compound appears rosy red so it is called rhodizonic acid. However, the three, four, and seven-membered ring members are called deltic, squaric, and haptagonic acids, respectively, after their shapes rather than colors. Scientific nomenclature usually stresses consistency, but this is a rather unusual exception.
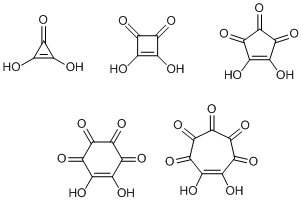
From the upper left, deltic acid, squaric acid, croconic acid, rhodizonic acid, and haptagonic acid
Green
I once thought that chlorophyll contained chlorine atoms because of how the name sounded. But needless to say, the molecule of chlorophyll is made up of C, H, O, N, and Mg, having nothing to do with Cl.
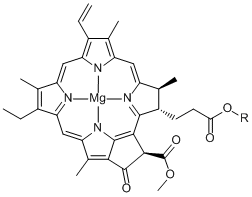
Chlorophyll a

Chlorogenic acid
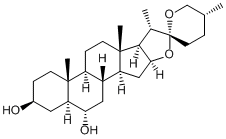
Chlorogenin
Introduction of the author
Kentaro Sato
[Specialty] Organic chemistry

