Maximum quantity allowed is 999

Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are crystalline organic frameworks consisting of a network structure made of covalent bonds.1,2) COFs are classified as porous crystalline materials similar to metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)/porous coordination polymers (PCPs) and zeolites. They include 2D COFs, which are constructed by stacking layers of 2D covalently bonded sheets, and 3D COFs, which are constructed by 3D connected frameworks. COFs are expected to be used as molecular storage or separation materials, catalysts, electronic materials, energy storage materials, battery materials, and drug delivery materials, due to their porosity, crystallinity, and structural diversity.
COFs are designed and synthesized by combining monomers, also called linkers, according to intended topology. TCI has more than 70 linkers in stock, and we are constantly adding new items to our catalog. Common linkers are shown below by functional groups.
Aldehyde Linkers
A type of COFs based on imine linkage, synthesized by condensation of aldehydes and amines, was first reported in 2009,3) and imine-based COFs have become the most widely reported COFs. One of the advantage of imine based COFs is their higher chemical stability compared to boroxines and boronate esters. In addition, a number of researchers have reported post-synthetic modification or functionalization of imine based COFs, e.g., COFs for CO2 capture were synthesized by post-synthetic modification and functionalization of imine-based structures.4) In 2012, β-ketoenamine-type COFs synthesized by using 2,4,6-triformylphloroglucinol (TPG, TFP) as an aldehyde linker were reported,5) and have recently attracted much attention because of their stability towards acids and bases.
Products
- T0010
- Terephthalaldehyde (= PDA)
- B2854
- 4,4'-Biphenyldicarboxaldehyde
- B6576
- [2,2'-Bipyridine]-5,5'-dicarbaldehyde
- D5510
- 2,5-Dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde
- D6056
- 2,5-Dimethoxyterephthalaldehyde
- T4088
- 2,3,5,6-Tetrafluoroterephthalaldehyde
- T3688
- 2,4,6-Triformylphloroglucinol (= TFP, TPG)
- D6046
- 2,4,6-Triformylresorcinol
- B6003
- 1,3,5-Triformylbenzene
- F1252
- 1,3,5-Tris(4-formylphenyl)benzene
- T4077
- 2,4,6-Tris(4-formylphenoxy)-1,3,5-triazine
Amine Linkers
Amine linkers are used to synthesize imine-linked COFs by condensation of aldehydes and amines as described in the aldehyde linkers section, as well as imide-linked COFs mentioned in the carboxylic anhydride linkers section below, and squaraine-linked COFs.6)
Products
- P0170
- 1,4-Diaminobenzene
- P1691
- 2,5-Diaminobenzenesulfonic Acid
- D2893
- [2,2'-Bipyridine]-5,5'-diamine
- D3180
- 2,6-Diaminoanthraquinone
- T2332
- Tris(4-aminophenyl)amine (= TAPA)
- T2728
- 1,3,5-Tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene (= TAPB)
- T3695
- 4,4',4''-(1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triyl)trianiline
- M3538
- 2,5,8-Triamino-1,3,4,6,7,9,9b-heptaazaphenalene
- T2947
- Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)methane
- T1494
- 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)porphyrin
Carboxylic Anhydride Linkers
Imide-linked COFs obtained by condensation of carboxylic anhydrides and amines have also been reported7) and are expected to be applied to battery materials8) and CO2 capture materials.9)
Products
- B0040
- Pyromellitic Dianhydride
- P2103
- Pyromellitic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
- N1128
- 2,3,6,7-Naphthalenetetracarboxylic 2,3:6,7-Dianhydride
- N0369
- Naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic Dianhydride
- N0755
- Naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
- N1247
- 1,2,5,6-Naphthalenetetracarboxylic Dianhydride
- P0972
- 3,4,9,10-Perylenetetracarboxylic Dianhydride
- P2102
- 3,4,9,10-Perylenetetracarboxylic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
- M3617
- Mellitic Trianhydride
Boronic Acid Linkers
The self-condensation of boronic acids to produce boroxines and the condensation of boronic acids and catechols to produce boronic esters are the first synthetic strategies to synthesize COFs.10)
Products
Other Linkers
COFs constructed by linkers other than imines, imides, and boroxines are realized. These COFs are prepared using linkers other than amines, aldehydes, carboxylic anhydrides, and boronic acids. For example, hydrazone-type COFs synthesized by hydrazines and aldehydes11,12) and ionic COFs synthesized using 1,2,3-triaminoguanidinium chloride13) are reported. β-ketoenamine-type COFs with improved crystallinity and surface area, derived by synthesis of precursors with urea linkage and following "reconstruction" of β-ketoenamine-type COFs, have been reported.14)
Products
- H0907
- 2,3,6,7,10,11-Hexahydroxytriphenylene (= HHTP)
- B6577
- 1,1'-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4,4'-diyl)diurea
- T0758
- Terephthalic Dihydrazide
- H0172
- Hydrazine Monohydrate
- H0697
- Hydrazine Anhydrous
- T4080
- 1,2,3-Triaminoguanidinium Chloride
- D1399
- Squaric Acid
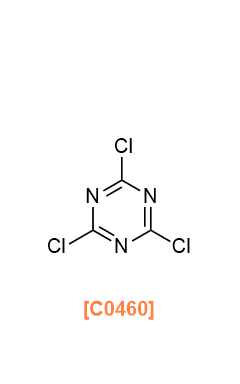
- C0460
- 2,4,6-Trichloro-1,3,5-triazine
- T4145
- 2,5,8-Trichloro-1,3,4,6,7,9,9b-heptaazaphenalene
- X0061
- 1,4-Phenylenediacetonitrile
- T0016
- Terephthalonitrile
Related Products
The following is a list of common reagents that are used as modulators to increase the crystallinity of the resulting COFs and as catalysts for the synthesis of COFs.
Modulators
Catalysts
Examples of COFs Synthesis
Synthesis of COF-300 3)

Synthesis of TpPa-1 5)

Synthesis of COF-1 10)

Synthesis of RC-COF-3 14)

Product Brochures
References
- 1) Covalent Organic Frameworks: Organic Chemistry Extended into Two and Three Dimensions
- 2) Covalent Organic Frameworks: Structures, Synthesis, and Applications
- 3) A Crystalline Imine-Linked 3-D Porous Covalent Organic Framework
- 4) Covalent Organic Frameworks for Carbon Dioxide Capture from Air
- 5) Construction of Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks with Remarkable Chemical (Acid/Base) Stability via a Combined Reversible and Irreversible Route
- 6) A Squaraine-Linked Mesoporous Covalent Organic Framework
- 7) Designed synthesis of large-pore crystalline polyimide covalent organic frameworks
- 8) Covalent Organic Framework with Highly Accessible Carbonyls and π-Cation Effect for Advanced Potassium-Ion Batteries
- 9) Synthesis, characterization, and CO2 uptake of mellitic triimide-based covalent organic frameworks
- 10) Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks
- 11) Crystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks with Hydrazone Linkages
- 12) Mechanosynthesis of imine, β-ketoenamine, and hydrogen-bonded imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using liquid-assisted grinding
- 13) Cationic Covalent Organic Framework Nanosheets for Fast Li-Ion Conduction
- 14) Reconstructed covalent organic frameworks


![[2,2'-Bipyridine]-5,5'-dicarbaldehyde](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/covalent_organic_frameworks_COFs_linkers_B6576.png)










![[2,2'-Bipyridine]-5,5'-diamine](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/covalent_organic_frameworks_COFs_linkers_D2893.png)

















![1,1'-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4,4'-diyl)diurea](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/covalent_organic_frameworks_COFs_linkers_B6577.png)