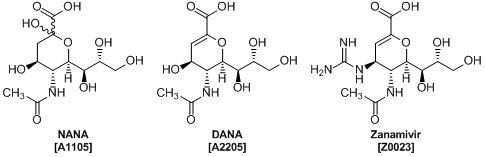
Influenza is an infectious disease caused by the influenza virus. The influenza virus has hemagglutinin, a glycoprotein on the surface of the viral particle. Hemagglutinin mediates the virus invasion by binding to N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA), a sialic acid on the animal cell membranes. The infected cells replicate the viral genes followed by the release of viral particles from the cells to spread the infection. When they are released, the neuraminidase on the outside of the viral particle acts as an enzyme cleaving the sialic acid groups at the infected cell surface.1,2)
It was revealed in the 1970s that 2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy-N-acetylneuraminic acid (DANA), a sialic acid analogue, inhibits the influenza virus neuraminidase.3,4) Since then, zanamivir, a DANA derivative developed through rational drug design, has been used as an influenza antiviral.5) New antivirals based on DANA as neuraminidase inhibitors are being investigated today.6)
Make sure to sign up for an account today for exclusive coupons and free shipping on orders over $75!