Three-dimensional (3D) covalent organic frameworks (COFs) and porous polymers are anticipated to be applicable for gas storage and separation, and as catalysts because of their high specific surface area and thermal stability. COFs are 2D or 3D covalently extended crystalline materials composed of light atoms.1,2)
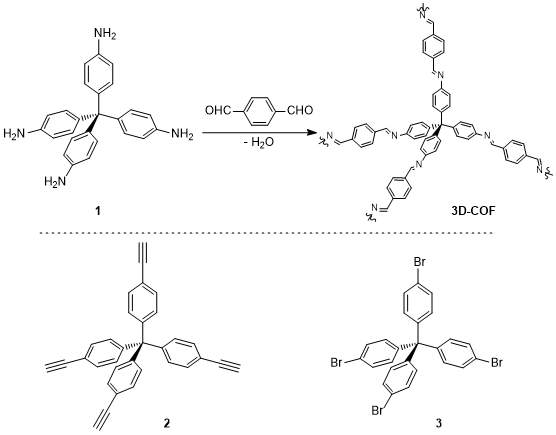
Yaghi et al. synthesized a 3D-COF by dehydration condensation of tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)methane (1) and terephthalaldehyde.3) The resultant COF was reported to have a diamond-like structure owing to the tetrahedral structure of 1.
Furthermore, building blocks with tetrahedral centers such as tetrakis(4-ethynylphenyl)methane (2) and tetrakis(4-bromophenyl)methane (3) are useful for producing porous polymers. Synthesis of porous polymers by click reactions4,5) and coupling reactions4,6) using 2 or 3 have been already reported.
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Please select the quantity
Tetrahedral Building Blocks for the Synthesis of 3D Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) and Porous Polymers
No.183(April 2020)
References
- 1)Chemistry of Covalent Organic Frameworks
- 2)Covalent Organic Frameworks: Chemistry beyond the Structure
- 3)A Crystalline Imine-Linked 3-D Porous Covalent Organic Framework
- 4)High Surface Area Networks from Tetrahedral Monomers: Metal-Catalyzed Coupling, Thermal Polymerization, and “Click” Chemistry
- 5)A “click-based” porous organic polymer from tetrahedral building blocks
- 6)Targeted Synthesis of a Porous Aromatic Framework with High Stability and Exceptionally High Surface Area
Related Compounds
The prices are subject to change without notice. Please confirm the newest price by our online catalog before placing an order.
In addition, sales products changes with areas. Please understand that a product is not available when the product details page is not displayed.
In addition, sales products changes with areas. Please understand that a product is not available when the product details page is not displayed.