In the field of biochemical research, buffering agents perform a very important function. The Tris buffers widely used today have a primary amino group and they are known to frequently cause inhibition problems in biological systems. Furthermore sufficient buffering power cannot be obtained under pH7.5.
Good and co-workers have developed buffers to overcome the above-noted defects and their superiority has been indicated by the Hill reactions. These buffers are referred to as Good’s Buffers being named after the inventor.
[Characteristics] 1) Acid dissociation constant p
Ka is between 6~8.
2) High water solubility.
3) Low penetration through biomembranes.
4) Low base effect toward biological systems.
5) p
Ka is less affected by concentration, temperature and ion composition.
6) Low complexation ability with metal ions.
7) Chemically stable.
8) Low in absorption of visible and ultra-violet rays.
Composition and pH range
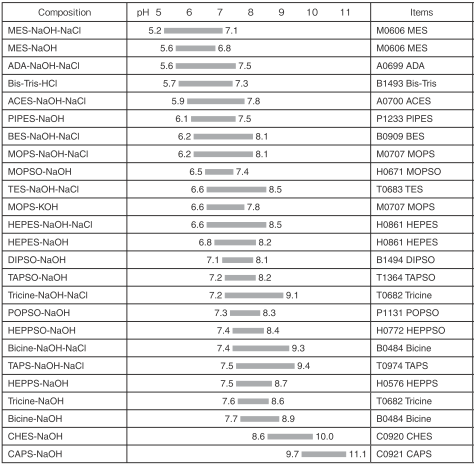
References
- N. E. Good, G. D. Winget, W. Winter, T. N. Connolly, S. Izawa, R. M. M. Singh, Biochemistry 1966, 5, 467.

- W. J. Ferguson, K. I. Braunschweiger, W. R. Braunschweiger, J. R. Smith, J. J. McCormick, C. C. Wasmann, N. P. Jarvis, D. H. Bell, N. E. Good, Anal. Biochem. 1980, 104, 300.



![N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/A0700.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8MjU5Nzh8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhREJqTDJoaU5TODRPVEk0TWpVeE5ERXlOVEV3TDBFd056QXdMbXB3Wnd8NTI0MmNmMzNmYmFlMzIxZGJjNWY4ZTBlYWUyMjg4MjNjMjRjYThhYjlkZDBkYzYwMDIxN2Q5NTQ4MDg2OTg0ZA)
![N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine [Good's buffer component for biological research] N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/structure-890-B0484.jpg-Tci-300?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8OTMyNXxpbWFnZS9qcGVnfGFEWTVMMmcwWkM4NU16WXpOVGt3T1RjeE5ESXlMM04wY25WamRIVnlaUzA0T1RBdlFqQTBPRFF1YW5CblgxUmphUzB6TURBfDNmZGM0ZTE2N2Q4YTM3ZTg1OTVmODViZGM3NTdhNjk4NzZkMGZlY2QyYTdjZDE0YWNhMTZjNTg3YThlNDgyOWQ)
![Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)aminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane [Good's buffer component for biological research] Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)aminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/B1493.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8Mzg2NDN8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhR1F4TDJneVpDODRPVEk0TmpZMk1USTBNekU0TDBJeE5Ea3pMbXB3Wnd8YjNlZGFlMGJjYzFiYzAzMzI4NDY4YzQ4ZWZlMGI1ZTg0ZWE4MjNhNDE4ZDU0OTBkZDQzZGZjMTEyOWZlZjU2NQ)
![2-Cyclohexylaminoethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] 2-Cyclohexylaminoethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/C0920.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8MzE1NzB8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhR0ZrTDJneE5pODRPVEk1TXpRNE9EYzRNelkyTDBNd09USXdMbXB3Wnd8NzkwNjI1MDk0YmNlYThiYmRlNWEzMTQwOTU5NzRhZGZhZDYzZTMyNDFjNmQ4NWM0ODQyZmE0ZTcwM2QxNzVjNw)
![2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] 2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/H0396.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8NDI1Mjh8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhRFV4TDJnM05pODRPVE13T0RjeU1EWTJNRGM0TDBnd016azJMbXB3Wnd8MzRlMWYyZjNiMTZjOTQ3ZDMzZWZlNjg3ZjkzOTI3NDA5YTllYTVjMGFjNTY3MzgyNGJmYzNiMTBhNTY1MjFkMw)
![Piperazine-1,4-bis(2-ethanesulfonic Acid) Monosodium Salt [Good's buffer component for biological research] Piperazine-1,4-bis(2-ethanesulfonic Acid) Monosodium Salt [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/P0875.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8NDQxMzZ8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhREprTDJoa1l5ODRPVE14T1RVM056TTFORFUwTDFBd09EYzFMbXB3Wnd8ZDNlZjU3ZTIxYmUwOWI3NmM3ZDA2MDE0OGVhMTYxODllYWY1NzBlNTI0YTdiMWM2ZWI5Nzk3Y2E2ZDE3MWQxNQ)
![Tricine [Good's buffer component for biological research] Tricine [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/T0682.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8MzIxMTd8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhRFEwTDJnM1l5ODRPVE15TXpZMk5qZ3dNRGswTDFRd05qZ3lMbXB3Wnd8YWM1Y2YzNDMxZmI1MWU1YTY1MDQwY2Q2MjcyYjRjNDcxMjhjMmE0YTBhYWMwYWFhMmI3YTgzYTc4ZTFlOGU5NA)
![3-[N-Tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]-2-hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] 3-[N-Tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]-2-hydroxypropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/T1364.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8MzA1ODl8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhR1l6TDJnd05DODRPVE15TkRNNE1qUTFOREEyTDFReE16WTBMbXB3Wnd8NzJiOTRlNzIxNjQ5ZTc3YzYzNDE3NTYxNTA1NjA4YzcwMWY2YTg2Yjc4YzQxMTAzYmVkMzI1MjFjNTIwMjYzYw)

![N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/B0909.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8MTQ2MjF8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhRFEwTDJoaU5DODVNalE1T0RrMk9Ea3dNems0TDBJd09UQTVMbXB3Wnd8MjFlMDY3ZDIzYzU3MzAxZGUxNGYxMmIwNjljYjg2NDU1ZWIxODA5ZDc0ZTdmZmMyMWRjY2MwNmM2MTNmMzYzNA)
![3-Cyclohexylaminopropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] 3-Cyclohexylaminopropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/C0921.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8Mjk2Mjl8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhRGxqTDJneE15ODRPVEk1TXpRNE9UUXpPVEF5TDBNd09USXhMbXB3Wnd8MTQ0Y2EwZjg3N2Q2NmI1NTg5ZjEyOTNjMzEyNDQ5NzMwOGY5NmE3NGQ1Yjk1ZGJlMmU4ZjBjYzc5NGM3NzU1Nw)
![4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinepropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research] 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinepropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component for biological research]](/medias/H0576.jpg?context=bWFzdGVyfHJvb3R8Mzg1NjB8aW1hZ2UvanBlZ3xhREZsTDJnM01TODRPVE13T0RneU56UTRORFEyTDBnd05UYzJMbXB3Wnd8ZGZmN2M0MGM1OTJhOTdlYzBiMGRiYTliZjcyMGEyNGM0YTBhMDMzMTZjZjdkM2FiNjYwNmY3ZWE3YjhiYTdiOA)