TCI uses cookies to personalize and improve your user experience. By continuing on our website, you accept the use of cookies. You can change or update your cookiesettings at any time.
Notice of Discontinuing the Use of Password-Protected Compressed Files|Product Document Searching Made Easy by 2D Code! | TCI Chemistry News November 2024 | [Product Highlights] Hypervalent Iodine Reagent... | Various analytical charts can be searched on each product detail page and Product Document Search (The kinds of analytical charts differ by product)
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Please select the quantity
Controlled Radical Polymerization Reagents

Controlled radical polymerization (CRP) or reversible-deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP), also known as living radical polymerization (LRP), has distinct advantages over conventional free radical polymerization. CRP techniques enable easier control over the molecular weight of the resulting polymers, enabling synthesis of polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions, and enabling synthesis of specialized structured polymers such as block copolymers, star shaped polymers, hyperbranched polymers, graft polymers, and bottlebrush polymers.
As the term "reversible-deactivation radical polymerization" suggests, CRPs are chain polymerization propagated by radicals that are reversibly deactivated and leading to active-dormant equilibria.1) When the concentration of active species is sufficiently low and the exchange rate between active and dormant species is faster than propagation, termination and irreversible chain transfer are suppressed and all polymer chains grow at the same rate.
In recent years, CRPs have been increasingly utilized in the development of functional materials and have also been adopted in industries.2)
We offer essential reagents for various CRPs, including reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization, atom-transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), organotellurium-mediated radical polymerization (TERP), organocatalyzed living radical polymerization including reversible complexation mediated polymerization (RCMP), and nitroxide-mediated polymerization (NMP).
Reversible Addition Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) Polymerization Reagents
===============================>>[SEE MORE]<<================================
In RAFT polymerization, thioester compounds, known as RAFT agents, are used as chain transfer agents (CTAs).2,3,4) Under typical conditions, thermal radical initiators such as AIBN are used as the radical source. Alternative methods that do not rely on thermal radical initiators have also been reported, including photoinduced electron transfer (PET) RAFT polymerization using photoredox catalysts5) and acid-triggered RAFT polymerization.6)
Examples of RAFT agent items
Product Category Page
Related Product Spotlight Page
Related Product Brochures
Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (ATRP) Reagents
===============================>>[SEE MORE]<<================================
In ATRP, active radical species are reversibly generated through the abstraction of halogen atoms from the organic halides (ATRP initiators and dormant spiecies).7,8,9) Metal-free ATRP using organocatalysts (O-ATRP) have also been developed.10)
Examples of ATRP initiator items
Examples of ATRP ligands items
Product Category Page
Related Product Spotlight Page
Related Product Brochures
Organotellurium-mediated Living Radical Polymerization (TERP) Reagents
===============================>>[SEE MORE]<<================================
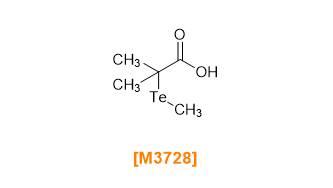
In TERP, organotellurium compounds are used as chain transfer agents (CTAs).11) One of its advantages is the broad range of monomers that can be controlled using the same chain transfer agent, simplifying the CTA selection.
Examples of Chain transfer agents (CTAs) for TERP
Product Category Page
Related Product Spotlight Page
Related Product Brochures
Organocatalyzed Living Radical Polymerization Reagents
===============================>>[SEE MORE]<<================================
Organocatalyzed living radical polymerization often employs alkyl iodides as initiators. Particularly in reversible complexation mediated polymerization (RCMP), organic salts like tetrabutylammoniumu iodide or alkali metal salts like sodium iodide are used as iodine anion catalyst sources,12) offering the advantage of avoiding heavy metals and sulfur compounds.
Examples of alkyl iodide initiator items
Product Category Page
Related Product Brochures
Nitroxide-Mediated Radical Polymerization (NMP) Reagents
===============================>>[SEE MORE]<<================================
In NMP, nitroxides such as TEMPO are used to reversibly convert active propagating radicals into dormant alkoxyamine species.13,14)
Examples of nitroxide items
Product Category Page
References
===============================>>[SEE MORE]<<================================
- 1) Terminology for reversible-deactivation radical polymerization previously called “controlled” radical or “living” radical polymerization (IUPAC Recommendations 2010)
- 2) 50th Anniversary Perspective: RAFT Polymerization—A User Guide
- 3) Living Radical Polymerization by the RAFT Process—A Third Update
- 4) Progress and Perspectives Beyond Traditional RAFT Polymerization
- 5) Photocontrolled RAFT polymerization: past, present, and future
- 6) Acid-triggered radical polymerization of vinyl monomers
- 7) Metal-Catalyzed Living Radical Polymerization
- 8) Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization
- 9) Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization: A Mechanistic Perspective
- 10) Photoinduced Organocatalyzed Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (O-ATRP): Precision Polymer Synthesis Using Organic Photoredox Catalysis
- 11) Precision Polymer Synthesis by Degenerative Transfer Controlled/Living Radical Polymerization Using Organotellurium, Organostibine, and Organobismuthine Chain-Transfer Agents
- 12) Recent Development in Halogen-Bonding-Catalyzed Living Radical Polymerization
- 13) New Polymer Synthesis by Nitroxide Mediated Living Radical Polymerizations
- 14) Nitroxide-Mediated Polymerization
![4-Cyano-4-[[(dodecylthio)carbonothioyl]thio]pentanoic Acid](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/reagents_for_controlled_radical_polymerizations_C3546.png)

![4-Cyano-4-[(phenylcarbonothioyl)thio]pentanoic Acid](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/reagents_for_controlled_radical_polymerizations_C3549.png)
![2-[[(Ethylthio)carbonothioyl]thio]-2-methylpropanoic Acid](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/reagents_for_controlled_radical_polymerizations_E1466.png)




![Tris[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amine](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/reagents_for_controlled_radical_polymerizations_T2898.png)