Caution Notice:
It has come to our notice that certain fraudulent individuals or entities are misusing our Company’s name and TCI’s registered trademarks by promoting and offering for sale regulated and hazardous chemical substances, including Potassium Cyanide, through online platforms like YouTube. We hereby categorically clarify that TCI has no association or connection whatsoever with the products being displayed or sold in these or similar videos. These products have been falsely represented as being associated with TCI, and the unauthorized use of our trademark and brand name is both illegal and misleading. TCI Chemicals is a responsible global organization committed to adhering to all applicable international and domestic regulatory frameworks. We do not manufacture, distribute, or engage in the sale of regulated chemical substances in India or in any other jurisdiction unless specifically authorized by the relevant laws and regulatory agencies. All our operations and offerings are governed by stringent safety, quality, and compliance protocols in accordance with applicable laws. Further, TCI Chemicals markets and sells its products exclusively through its official website and authorized distributors. We do not sell, endorse, or supply our products through any third-party platforms, unauthorized agents, or resellers. Any individual or organization purchasing products outside these official channels does so at their own risk, and TCI disclaims all responsibility and liability for any consequences arising therefrom. Members of the public, customers, and partners are strongly advised to exercise caution and conduct due diligence before engaging in any transactions involving products claiming association with TCI Chemicals. The official list of our authorized distributors is publicly available and may be accessed at: https://www.tcichemicals.com/IN/en/distributor/index. We are currently pursuing appropriate legal remedies against those misusing our brand, and we reserve all rights available to us under applicable intellectual property and criminal laws. If you become aware of any such fraudulent activity or require clarification, you may reach out to us at: Sales-IN@TCIchemicals.com. Your vigilance and cooperation are essential in safeguarding the public interest and protecting the integrity of the TCI brand.
TCI uses cookies to personalize and improve your user experience. By continuing on our website, you accept the use of cookies. You can change or update your cookiesettings at any time.
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Please select the quantity
Protein Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is a technique which separates charged biomolecules based on the rate at which they migrate in an applied electrical field. In many cases, electrophoresis of proteins are performed using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE).1) For molecular weight estimation and purity determination of proteins, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-PAGE is frequently employed. SDS is a strong denaturant of proteins and is added to samples, gels, and buffer solutions for electrodes when proteins are separated with electrophoresis. As SDS not only denatures protein but also binds to the protein, when SDS is used in conjunction with a reducing reagent such as 2-mercaptoethanol to cleave disulfide bonds in the protein, and the protein is completely denatured, the amount of SDS bound is almost always proportional to the molecular weight of the protein. Resultantly, the protein is negatively charged. Therefore, the denatured protein can be separated by molecular weight independently of its structure and biological properties.
Laemmli’s method is the most widely used system of SDS-PAGE.2) In this method, the separation and the stacking gel contain Tris-HCl and the upper and lower buffer reservoirs contain Tris-glycine. All components of the system contain SDS. The advantage of Laemmli’s method is that it gives sharper bands in the final plate.1)
Laemmli’s method is the most widely used system of SDS-PAGE.2) In this method, the separation and the stacking gel contain Tris-HCl and the upper and lower buffer reservoirs contain Tris-glycine. All components of the system contain SDS. The advantage of Laemmli’s method is that it gives sharper bands in the final plate.1)

[Example of electrophoresis]
Concentration of gel for separation: 7.5%
Staining: Ag-staining
Sample proteins: commercially available molecular weight marker
Lane 1: 250 ng
Lane 2: 62.5 ng
Lane 3: 16 ng
Lane 4: 4 ng
Lane 5: 0 ng
■Typical Procedure
CBB R-250 staining of separated proteins on SDS-PAGE
Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (CBB R-250) is frequently used for protein staining after PAGE.
Solutions
CBB R-250 staining solution: 0.25% CBB R-250, 50% methanol, 10% acetic acid Destaining solution: 50% methanol, 10% acetic acid
Procedure
1. Soak gel after electrophoresis in CBB R-250 staining solution with gentle agitation for 1 h.
2. Transfer the gel after step 1 into the destaining solution and gently agitate for 10 min.
3. Destain the gel until it gives an appropriate stained image by changing the destaining solution several times.
4. After destaining, transfer the gel into pure water and gently agitate for 1 h.
■Typical Procedure
Fast Green FCF staining of separated proteins on SDS-PAGE3)
Fast Green FCF is used for staining and determination of protein after PAGE, SDS-PAGE etc. Stained protein is detected by absorbance at 625nm and quantified.
Solutions
Fast Green FCF staining solution: 0.1% Fast Green FCF, 30% ethanol, 10% acetic acid
Destaining solution: 30% ethanol, 10% acetic acid
Procedure
1. Soak gel after electrophoresis in Fast Green FCF staining solution with gentle agitation for 1 h.
2. Transfer the gel after step 1 into the destaining solution and gently agitate for 10 min.
3. Destain the gel until it gives an appropriate staining image by changing the destaining solution several times at 10-minute intervals.
4. After destaining, transfer the gel into pure water and gently agitate for 1 h.
Concentration of gel for separation: 7.5%
Staining: Ag-staining
Sample proteins: commercially available molecular weight marker
Lane 1: 250 ng
Lane 2: 62.5 ng
Lane 3: 16 ng
Lane 4: 4 ng
Lane 5: 0 ng
■Typical Procedure
CBB R-250 staining of separated proteins on SDS-PAGE
Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (CBB R-250) is frequently used for protein staining after PAGE.
Solutions
CBB R-250 staining solution: 0.25% CBB R-250, 50% methanol, 10% acetic acid Destaining solution: 50% methanol, 10% acetic acid
Procedure
1. Soak gel after electrophoresis in CBB R-250 staining solution with gentle agitation for 1 h.
2. Transfer the gel after step 1 into the destaining solution and gently agitate for 10 min.
3. Destain the gel until it gives an appropriate stained image by changing the destaining solution several times.
4. After destaining, transfer the gel into pure water and gently agitate for 1 h.
■Typical Procedure
Fast Green FCF staining of separated proteins on SDS-PAGE3)
Fast Green FCF is used for staining and determination of protein after PAGE, SDS-PAGE etc. Stained protein is detected by absorbance at 625nm and quantified.
Solutions
Fast Green FCF staining solution: 0.1% Fast Green FCF, 30% ethanol, 10% acetic acid
Destaining solution: 30% ethanol, 10% acetic acid
Procedure
1. Soak gel after electrophoresis in Fast Green FCF staining solution with gentle agitation for 1 h.
2. Transfer the gel after step 1 into the destaining solution and gently agitate for 10 min.
3. Destain the gel until it gives an appropriate staining image by changing the destaining solution several times at 10-minute intervals.
4. After destaining, transfer the gel into pure water and gently agitate for 1 h.
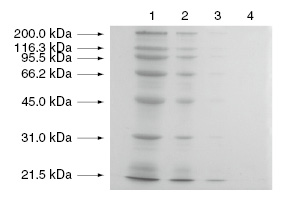
[Example of staining]
Concentration of gel for separation: 10%
Staining: Ag-staining
Sample proteins: commercially available molecular weight markers
Lane 1 : 4 μg
Lane 2 : 0.8 μg
Lane 3 : 0.16 μg
Lane 4 : 0 μg
■Typical Procedure
Reversible protein staining with Acid Red 112 (Ponceau-S)4)
Acid Red 112 gives a pinkish staining image. Because the staining with the dye is reversible and the dye can be removed from stained protein, immunoassay and other analyses can be carried out after destaining.
Solution
Acid Red 112 staining solution: 0.1% Acid Red 112, 5% acetic acid
Procedure
1. Soak the protein-blotted membrane into Acid Red 112 staining solution and gently agitate for 2 min.
2. Transfer the membrane into pure water and destain until it gives an appropriate staining image.
3. When required to completely remove the dye from the stained protein, gently agitate the membrane in 0.1mol/L NaOH.
Concentration of gel for separation: 10%
Staining: Ag-staining
Sample proteins: commercially available molecular weight markers
Lane 1 : 4 μg
Lane 2 : 0.8 μg
Lane 3 : 0.16 μg
Lane 4 : 0 μg
■Typical Procedure
Reversible protein staining with Acid Red 112 (Ponceau-S)4)
Acid Red 112 gives a pinkish staining image. Because the staining with the dye is reversible and the dye can be removed from stained protein, immunoassay and other analyses can be carried out after destaining.
Solution
Acid Red 112 staining solution: 0.1% Acid Red 112, 5% acetic acid
Procedure
1. Soak the protein-blotted membrane into Acid Red 112 staining solution and gently agitate for 2 min.
2. Transfer the membrane into pure water and destain until it gives an appropriate staining image.
3. When required to completely remove the dye from the stained protein, gently agitate the membrane in 0.1mol/L NaOH.

[Example of staining]
Bovine serum albumin, with the amount shown in the figure, is spotted on a nitrocellulose membrane and stained with Acid Red 112.
References
- 1)J. Sambrook, D. W. Russell, in Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 2001.
- 2)U. K. Laemmli, Nature 1970, 227, 680.

- 3)M. J. Bertolini, D. L. Tankersley, D. D. Schroeder, Anal. Biochem. 1976, 71, 6.

- 4)R.Simpson, in Proteins and Proteomics, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 2003.
- Home
- Products
- Life Science
- Molecular Biology
- Proteomics
- Protein Electrophoresis

