Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.197
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Please select the quantity
Palladium Catalysts
No.103(July 1999)

The present reagent 1 serves as a catalyst in the reaction of aromatic halide with amine under a pressurized carbon monoxide atmosphere to form carbonyl compounds. For example, this catalyst can catalyze the reaction of o-diiodobenzene with primary amines, resulting in the formation of N-substituted phthalimides1). This catalyst tolerates a wide variety of functional groups . Formation of a wide spectrum of products in high yields is possible. In addition, it catalyzes the reaction of aromatic monohalides with secondary amines to form α-ketoamides and amides2). The α-ketoamides are useful intermediates synthesizing α-amino acids or α-hydroxycarboxylic acids.
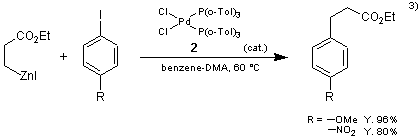
The present reagent 2 catalyzes the coupling reaction of the organozinc reagents with aryl iodides to form the products in high yields. In the conventional method, using dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) or tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) as a catalyst, biaryl, byproduct, are formed, but use of the present reagent 2 suppresses the formation of biaryl.
References
- 1) Preparation of N-substituted phthalimides by the Pd-catalyzed carbonylation
- 2) Pd-catalyzed double carbonylation of aryl halides
- 3) The coupling reaction of organozinc reagents with aryl iodides
- 4) Other applications
- a) 1-Alkenylation on α-position of ketones
- b) α-Phenylation of ketones
The prices are subject to change without notice. Please confirm the newest price by our online catalog before placing an order.
In addition, sales products changes with areas. Please understand that a product is not available when the product details page is not displayed.
In addition, sales products changes with areas. Please understand that a product is not available when the product details page is not displayed.

