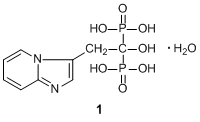
Bisphosphonates (BPs), including minodronate, ibandronate, etc., are very effective inhibitors of bone resorption in vivo and in vitro. Minodronate monohydrate (1) is one of BPs.1,2) These compounds are characterized by two C-P bonds which are located on the same carbon atom, i.e. geminal BPs, and have been used for many research studies regarding bone metabolism.1,2)
According to differences in the side chain, BPs can be divided into two groups, non-nitrogen containing BPs (non-N-BPs) and nitrogen-containing BPs (N-BPs). 1 is a N-BP and is classified as a third-generation heterocyclic N-BP.2,3) N-BPs inhibit farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase, a key enzyme in the mevalonate pathway, which affects cellular activity and survival.1,2) Regarding inhibition of bone resorption, 1, as well as zoledronic acid, is more effective than other BPs.4)
Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.197