Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.197
Maximum quantity allowed is 999

Neutral Polysaccharides
Neutral polysaccharides are composed of neutral monosaccharides such as glucose and xylose linked by glycosidic bonds and are polymerized as macromolecules in the range of thousands to millions. They are known to exhibit various properties depending on the type of composed monosaccharides, the bonding position, the presence / absence of side chains / branches, and so on. Since these polysaccharides have many hydroxyl groups (OH), they show affinity for water molecules. they act as hydrophilic colloids holding a large number of water molecules due to their properties. For industrial use, they are widely used for various purposes such as dispersion stabilization, suspension stabilization, viscosity imparting, gel-forming ability, film-forming feature, and adhesive effect.1)

| Product No. | Product Name | Main Chain linkages ‡ | Constituent Monosaccharides ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0456 | Amylopectin | α1-4, [Branches α1-6] | Glc |
| D1449 | Dextran | α1-6 | Glc |
| L0088 | Laminaran | β1-3, [Branches β1-6] | Glc |
| P0978 | Pullulan | α1-4 and α1-6 | Glc α1-6 bonds of (Glcα 1-4 Glc α1-4 Glc) unit |
| X0078 | Xylan | β1-4, [Side chains α1-2, α1-3] | Main chains: Xyl Side chains: Ara, 4-O-Me-GlcA |
| C0072 | Chitin | β1-4 | GlcNAc |
‡Since polysaccharides are heterogeneous compounds, representative main chain linkages and constituent monosaccharides are shown.
Products
- A0456
- Amylopectin (Amylose free), from Waxy Corn
- A1328
- (+)-Arabinogalactan from Larch Wood
- C0072
- Chitin
- D1448
- Dextran 40 (Mw.=ca. 40,000)
- D1449
- Dextran 70 (Mw.=ca. 70,000)
- D4657
- Dextrin
- D5658
- Dextrin (Soluble fiber)
- G0331
- Glucan from Black Yeast
- G0478
- Guar Gum
- I1067
- Inulin (by Enzymatic synthesis)
- L0088
- Laminaran from Eisenia Bicyclis
- P0978
- Pullulan
- T0909
- Tamarind Gum from Tamarind seed, Polysaccharide
- X0078
- Xylan from Corn Core
Acidic Polysaccharides
Acidic polysaccharides contain a lot of uronic acids (a compound in which the terminal hydroxy group [-CH2OH] of aldohexose is oxidized to a carboxy group [-COOH]) and several sulfate groups (a compound in which the hydroxy group [-OH] of aldohexose is dehydrated condensation with sulfuric acid). These polysaccharides are thought to function with mechanisms that maintain the structure of plant tissues and protect them from exogenous substances. Polyuronic acid-containing pectin and gum arabic are found in land plants while polyuronic acid-containing alginic acid, sulfate group-containing carrageenan and fucoidan are obtained from seaweeds. For practical use, they are widely used for purposes such as imparting viscosity, adhesive effect, dispersion stabilization, aggregation suppression, protein stabilization, and gel-forming ability.2)

| Product No. | Product Name | Main Chain linkages ‡ | Constituent Monosaccharides ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0733 | Alginic Acid | β1-4 | ManA, GulA |
| P0024 | Pectin | α1-4 | GalA, GalA[COOMe] |
| X0048 | Xanthan Gum | β1-4, [Side chains α1-3] | Main chains: Glc Side chains: Man, GlcA |
| C1804 | κ-Carrageenan | α1-3Gal(4S)β1-4Anhydro-Gal | Gal(4S), 3,6-Anhydro-Gal |
| C1805 | ι-Carrageenan | α1-3Gal(4S)β1-4Anhydro-Gal(2S) | Gal(4S), 3,6-Anhydro-Gal(2S) |
| C3313 | λ-Carrageenan | α1-3Gal(2S)β1-4Gal(2S, 6S) | Gal(2S, 6S), Gal(2S) |
‡Since polysaccharides are heterogeneous compounds, representative main chain linkages and Constituent monosaccharides are shown. The sulfate group in paren thesis is the OH position that can be introduced.
Products
- A0733
- Alginic Acid
- A0205
- Alginic Acid Sodium Salt 100-200
- O0583
- Alginic Acid Sodium Salt 300-400
- O0584
- Alginic Acid Sodium Salt 500-600
- O0585
- Alginic Acid Sodium Salt 800-900
- A0738
- Alginic Acid Calcium Salt
- C1804
- κ-Carrageenan
- C1805
- ι-Carrageenan
- C2871
- λ-Carrageenan (Low-viscosity)
- C3313
- λ-Carrageenan (High-viscosity)
- P0024
- Pectin from Citrus
- X0048
- Xanthan Gum
Acidic Polysaccharides (Glycosaminoglycans)
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are long linear polysaccharides that form repeating disaccharide structures and have long been studied as systematic names for mucopolysaccharides. It is well known that it functions as a molecule of the extracellular matrix to support tissues present throughout the body. Due to their negative charge and binding to bioactive molecules, GAGs are intimately involved in the regulation of many cellular functions. In vivo, hyaluronic acid (HA) generally exists as a free sugar chain, but chondroitin sulfate (CS), dermatan sulfate (DS), keratan sulfate (KS), and heparan sulfate (HS) have sulfate group modifications in their internal structures, bind to coreproteins as side chains varying lengths. GAG-modified protein molecules are called proteoglycans (PG).3)


| Product No. | Product Name | Main Chain linkages ‡ | Constituent Monosaccharides ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1791 | Hyaluronic Acid Sodium Salt | β1-4GlcAβ1-3GlcNAc | GlcNAc, GlcA |
| D3672 | Dermatan Sulfate Sodium Salt | β1-4IdoAβ1-3GalNAc(4S) | GalNAc(4S), IdoA |
| C0335 | Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium Salt | β1-4GlcAβ1-3GalNAc(4S or 6S) | GalNAc(4S or 6S), GlcA |
| H0393 | Heparin Sodium Salt | α1-4GlcA or IdoA(2S)β1-3GlcNAc(NS, 3S, 6S) | GlcNAc(NS, 3S, 6S), GlcA, IdoA(2S) |
‡Since polysaccharides are heterogeneous compounds, representative main chain linkages and constituent monosaccharides are shown. And the sulfate group in paren thesis is the OH position that can be introduced.
Products
- C0335
- Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium Salt
- D3672
- Dermatan Sulfate Sodium Salt
- H0393
- Heparin Sodium Salt from Hog intestine
- H0595
- Hyaluronic Acid from Cockscomb
- H0603
- Hyaluronic Acid Sodium Salt from Cockscomb
- H0652
- Hyaluronic Acid Potassium Salt from Cockscomb
- H1807
- Hyaluronic Acid from Bacteria
- H1791
- Hyaluronic Acid Sodium Salt from Bacteria
- H1808
- Hyaluronic Acid Potassium Salt from Bacteria
Chemically Modified Polysaccharides (Sulfated Polysaccharides)
Sulfated polysaccharides are known as multifunctional polysaccharides, that are related in physiological functions on the cell surface in vivo. These polysaccharides have supportive effects of viral infections. It has been reported that chemical mimics of sulfated polysaccharides inhibit viral adhesion during infection step.4)

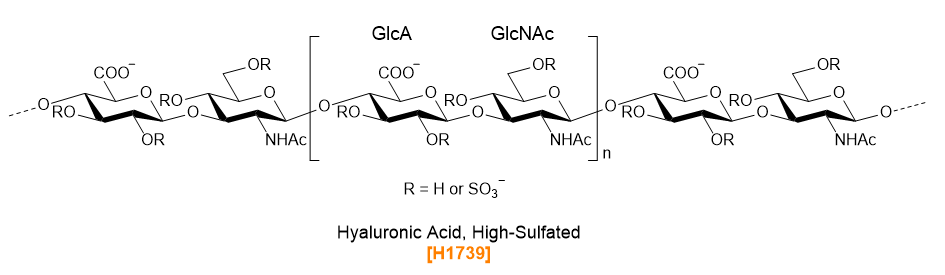
| Product No. | Product Name | Main Chain linkages ‡ | Constituent Monosaccharides ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1739 | Hyaluronic Acid, High-Sulfated | β1-4GlcA(2S, 3S)β1-3GlcNAc(4S, 6S) | GlcNAc(4S, 6S), GlcA(2S, 3S) |
| D5144 | Dextran Sulfate Sodium | Glc(2S, 3S, 4S)α1-6Glc(2S, 3S, 4S) | Glc(2S, 3S, 4S) |
‡Since polysaccharides are heterogeneous compounds, representative main chain linkages and constituent monosaccharides are shown and the sulfate group in paren thesis is the OH position that can be introduced.
Products
Other Chemically Modified Polysaccharides
Products
- C0045
- Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium (n=approx. 500)
- C0603
- Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium (n=approx. 1,050)
- C3250
- Carboxymethyldextran Sodium Salt (Mw.=ca. 10,000)
- C3251
- Carboxymethyldextran Sodium Salt (Mw.=ca. 40,000)
- E0265
- Ethyl Cellulose [9-11mPa·s, 5% in Toluene + Ethanol (80:20) at 25゚C]
- E0072
- Ethyl Cellulose [18-22mPa·s, 5% in Toluene + Ethanol (80:20) at 25゚C]
- E0266
- Ethyl Cellulose [45-55mPa·s, 5% in Toluene + Ethanol (80:20) at 25゚C]
- E0290
- Ethyl Cellulose [90-110mPa·s, 5% in Toluene + Ethanol (80:20) at 25゚C]
- F0918
- Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Dextran (Mw.=ca. 10000)
- H0242
- Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (200-300mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- H0418
- Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (800-1,500mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- H0392
- Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (4,500-6,500mPa·s, 2% in Water at 25゚C)
- H0473
- Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (3-6mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- H0474
- Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (6-10mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- H0386
- Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (150-400mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- H0475
- Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (1,000-4,000mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0290
- Methyl Cellulose (13-18mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0291
- Methyl Cellulose (20-30mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0292
- Methyl Cellulose (80-120mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0293
- Methyl Cellulose (350-550mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0294
- Methyl Cellulose (1,000-1,800mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0185
- Methyl Cellulose (3,500-5,600mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
- M0295
- Methyl Cellulose (7,000-10,000mPa·s, 2% in Water at 20゚C)
References
- 1) Role of polysaccharides in food, digestion, and health
- 2) Acidic Polysaccharides Having Biological Activities
- 3) Glycosaminoglycans and human diseases
- 4) Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias?

