Make sure to sign up for an account today for exclusive coupons and free shipping on orders over $75!
Maximum quantity allowed is 999

In discovery research on small molecule drugs, drug designs with high sp3 carbon content are preferred in order to improve flat structures, metabolic stability, hydrophilicity, off-target effect and so on.1) Furthermore, replacement of benzene cores with the bioisosteres, which is benzene equivalents containing rich sp3 carbons is popular.2) When carrying out such research, C(sp2)-C(sp3) cross coupling reactions are very powerful methods. These reactions enable direct introduction of alkyl groups into aromatic core. Recently, various methods not relying on organometallic reagents have been reported, in which alkyl halides, alkyl carboxylic acids etc. are used as alkyl sources. Especially, the cross coupling reactions between aryl halides and alkyl halides are known as reductive cross-electrophile coupling reactions (CEC, XEC), which attract a lot of attentions from a view point of availability and stability of alkyl halides.3) In addition, by achieving difficult introduction of alkyl groups it can be expected to create novel bioactive compounds.
Bidentate ligands such as bipyridyl derivatives have been widely used for nickel catalysis in the conventional reductive cross-electrophile coupling reactions.4) However, due to synthetic complexities, it is not easy to tune their steric and electronic properties. On the other hand, di(2-picolyl)amine (DPA) ligands can be sterically and electronically modified by optimizing the alkyl groups on nitrogen atom and substituents on pyridine rings.5) We offer three DPA ligands for reductive cross-electrophile coupling reactions.
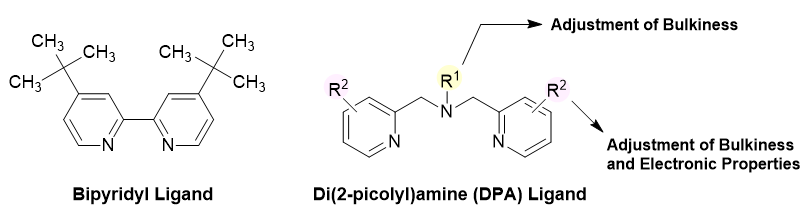
When DPA ligands are used as catalysts for reductive cross-electrophile coupling reactions, it is reported that better results can be obtained than the standard ligand, dtbbpy (Product No. D3134). In general, substituents on pyridine ring of DPA ligands favor electron rich groups and substituents on nitrogen atom give better results. In particular, it is known that secondary alkyl bromides such as heterocyclic alkyl bromides and etc. than primary alkyl bromides. DPA ligands have been found to improve the product yields from some substrates. In addition, our products are useful for late-stage functionalization, parallel library synthesis and high-throughput experiments (HTE) in the drug discovery research.
Products
Advantages
- Useful for C(sp2)-C(sp3) cross coupling reactions between aryl bromides and alkyl bromides
- Also applicable to secondary alkyl bromides such as heterocyclic alkyl bromides and etc.
- Suitable for parallel library synthesis and high-throughput experiments
We have a wide range of products such as many catalysts and building blocks, which are in line with the latest trends of medicinal chemistry. It would be our pleasure if our reagents are used for your successful research.
Related Products
- N1051
- Dichloro(glyme)nickel (= NiCl2(DME))
- N1298
- Dibromo(glyme)nickel (= NiBr2(DME))
- Z0015
- Zinc (Powder)
- S0564
- Sodium Iodide (= NaI)
- T0431
- Trifluoroacetic Acid (= TFA)
- P3015
- Pyridine-2,6-dicarboximidamide Dihydrochloride (= PyBCam·HCl)
- D6070
- N2,N6-Dicyanopyridine-2,6-bis(carboximidamide) (= PyBCamCN)
- P2176
- Pyridine-2-carboximidamide Hydrochloride (= PyCam·HCl)
- C3801
- N'-Cyano-2-pyridinecarboximidamide (= PyCamCN)
- C3803
- 4,4'-Di-tert-Butyl-N-cyano[2,2'-bipyridine]-6-carboximidamide (= tBuBpyCamCN)
Related Product Spotlight Pages
Related Product Category Pages
References
- 1) Improvements in Aqueous Solubility in Small Molecule Drug Discovery Programs by Disruption of Molecular Planarity and Symmetry
- 2) Bioisosteres of the Phenyl Ring: Recent Strategic Applications in Lead Optimization and Drug Design
- 3) Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Aryl Halides with Alkyl Halides: Ethyl 4-(4-(4-methylphenylsulfonamido)-phenyl)butanoate
- 4) Replacing Conventional Carbon Nucleophiles with Electrophiles: Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Alkylation of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides
- 5) Di(2-picolyl)amines as Modular and Robust Ligands for Nickel-Catalyzed C(sp2)−C(sp3) Cross-Electrophile Coupling



![1-(4-Methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)-N-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]-N-methylmethanamine](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/dipicolylamine_ligands_for_reductive_cross-electrophile_coupling_M3633.png)
![N,N-Bis[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]cyclopropanamine](https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-images/dipicolylamine_ligands_for_reductive_cross-electrophile_coupling_B6525.png)
