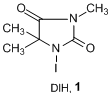
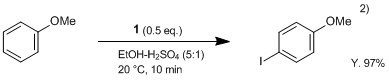
Typical Procedure:
2)Sulfuric acid (2 mL) is added under stirring and cooling to a solution of anisole (1.1 g, 10 mmol) in ethanol (15 mL), and DIH (
1; 1.9 g, 5 mmol) is then added in 3 portions over a period of 2-3 min. When the reaction is complete, the mixture is diluted with 3% solution of Na
2SO
3 (50 mL), and the precipitate is filtered off, washed with water, dried, and recrystallized from appropriate solvent. Yield of 4-iodoanisole 97%.