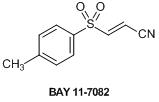
NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa B) is an intracellular protein complex that controls gene transcription, which was identified by D. Baltimore et al. in 1986.1) NF-κB is usually sequestered in the cytoplasm by forming an inactivated complex with IκB (Inhibitor κB). IKK (IκB kinase) activated by extracellular signals phosphorylates IκBα, and then the proteasome degrades phosphorylated IκBα. Then NF-κB can translocate into the nucleus and induce the expression of genes encoding molecules related to inflammatory immune response, apoptosis-suppressing molecules, cytostatic molecules, etc.2)
BAY 11-7082 is a small molecule inhibiting the phosphorylation of IκBα by IKK.3) It has been reported to use BAY 11-7082 as a NF-κB inhibitor in research of cancer, inflammation, viral infection and so on.4-7)
Maintenance Notice (5:15 AM - 4:55 PM May 24, 2025): This website is scheduled to be unavailable due to maintenance. We appreciate your patience and understanding.
Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.197