Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.199
Maximum quantity allowed is 999
Merci de sélectionner la quantité
Ireland-Claisen rearrangement
The Ireland-Claisen rearrangement is a modification of Claisen rearrangement resulting in γ,δ-unsaturated carboxylic acids from allyl esters. In this reaction, a substrate is treated with a silyl halide and a strong base to generate the silyl ketene acetal in situ, and affords the corresponding carboxylic acid through [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement. When generating the silyl ketene acetal, the E-enolate and the Z-enolate can be formed separately, which causes to control the stereochemistry of the product. Furthermore, it is considered that the transition state changes according to the allyl alcohol moiety, namely whether it is cyclic or acyclic, and that influences the expected stereochemistry of the product. The Ireland-Claisen rearrangement is similar to the Eschenmoser-Claisen rearrangement and the Johnson-Claisen rearrangement when used according to the proper choice of substrates and conditions.
- Reagents:
- Organic bases, Chlorosilanes
- Reactants:
- Allyl esters
- Products:
- γ,δ-Unsaturated carboxylic acids
- Scheme:
-
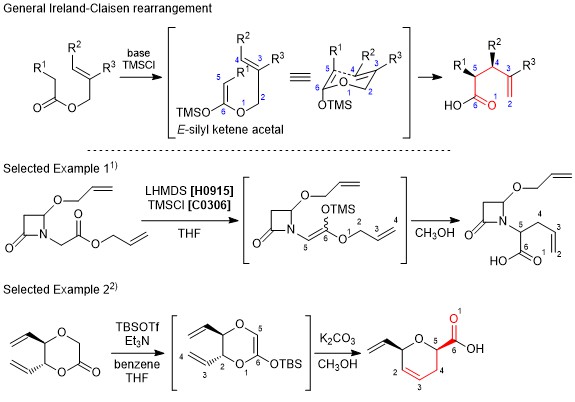
- Original literature:
-
- Claisen rearrangement of allyl esters
- Review literature:
-
- Claisen Rearrangement over the Past Nine Decades
- New aspects of the Ireland and related Claisen rearrangements

