Maintenance Notice (5:15 AM - 4:55 PM May 24, 2025): This website is scheduled to be unavailable due to maintenance. We appreciate your patience and understanding.
Published TCIMAIL newest issue No.198
Maximum quantity allowed is 999

Professor David R. Stuart

Unsymmetrical Aryl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium Tosylate Salts
Diaryliodonium salts are versatile compounds that have found use as photo-acid generators in polymer synthesis and as arylation reagents in small molecule synthesis; metal-free reactions have become increasingly popular with the respect to the latter.1 Unsymmetrical aryl(auxiliary)iodonium salts are particularly attractive as they permit the transfer of more elaborate aryl moieties and minimize aryl waste streams by employing readily available and recoverable auxiliaries. Trimethoxybenzene-derived auxiliaries have been regarded as a promising auxiliary for chemoselective transfer of the other aryl group yet synthetic access to these reagents has remained limited. The Stuart Research Group has recently developed a one-pot synthesis of aryl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium tosylate salts and demonstrated that these nascent arylation reagents selectively transfer the aryl group to C-, N-, O-, and S-nucleophiles.2 Several features make these appealing reagents: free-flowing bench-stable powders at ambient temperature; stable indefinitely when stored away from light; and react with diverse nucleophiles without the need for additional catalyst or inert atmosphere under mild conditions. The iodonium tosylate salts also serve as linchpin reagents to access salts with a variety of other counter anions, such as bromide, iodide, triflate, tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, and trifluoroacetate.
References
1 Merritt, E. A.; Olofsson, B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2009, 48, 9052-9070. Seidl, T.
2 L.; Sundalam, S. K.; McCullough, B.; Stuart, D. R. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 1998-2009.
O-Arylation of phenols

[Experimental procedure] 4-Fluorophenol (0.83 mmol, 1 equiv.) and potassium tert-butoxide (1.1 equiv.) were added to a vial containing a stir bar and toluene (3.3 mL) was added via syringe. The vial was capped and stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes. The cap was then removed and 4-biphenyl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium triflate (1.2 equiv.) was added as a powder in one portion. The vial was recapped and placed in a pre-heated aluminum block (40 °C) for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was partitioned between water and dichloromethane and the aqueous phase further extracted with dichloromethane. The combined organic fractions were dried with magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude residue was purified by column chromatography and the product isolated in 80% yield.
Initial conditions with symmetrical diaryliodonium triflate salts: Jalalian, N.; Ishikawa, E. E.; Silva, L. F. Jr.; Olofsson, B. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1552-1555
With aryl(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)iodonium triflate: Seidl, T. L.; Sundalam, S. K.; McCullough, B.; Stuart, D. R. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 1998-2009.
N-Arylation of sodium azide

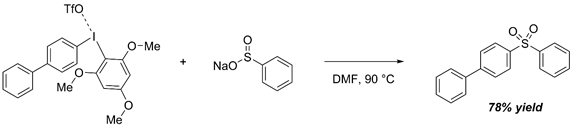
S-Arlyation of sodium phenyl sulfinate